
Citizens Save Their Town: Brewery, Sauna, and Cultural Center Run by the People
While many small towns are losing their last pub, Freyung in Bavaria is telling a different story. Locals saved their Läs mer…
Nyheter och länkar - en bra startsida helt enkelt |Oculus lyx vitae

While many small towns are losing their last pub, Freyung in Bavaria is telling a different story. Locals saved their Läs mer…

While many countries struggle to contain housing costs, Austria is setting an example of how governments can step in to Läs mer…

In the Bavarian village of Amerang, distances are long and buses rarely run. So, is it possible to live in Läs mer…

Wikipedia has been under attack. Right-wing extremists tried to change history, twist facts, and spread their own version of the truth. But they didn’t expect the pushback. This is the story of how the Wikipedia community came together to defend the truth—and won.
The Secret Plot to Rewrite History
In 2007, a sharp-eyed Wikipedia user named “Eintragung ins Nichts” (“Entry into Nothingness”) noticed something strange. A group of accounts was repeatedly editing articles about World War II, right-wing extremism, and antifascism. Their changes weren’t minor—they were designed to rewrite history.
The method? “Sockpuppets“—multiple fake accounts controlled by a single group—were used to make it seem like there was widespread agreement on false information. One of the biggest attempts was to introduce the term “Red Holocaust,” a phrase pushed by far-right groups to equate Nazi crimes with communist actions, watering down Germany’s responsibility for the war.
Wikipedia’s Community Fights Back
But Wikipedia’s volunteers refused to let misinformation win. Editors and administrators launched an investigation using special tools to track suspicious accounts. What they uncovered was shocking: more than 700 fake accounts were working together to spread false narratives.
Over three years, the Wikipedia community fought back, banning these accounts one by one. But the attackers didn’t stop. They created new accounts, found new ways to manipulate pages, and continued their attempts to twist history. What made Wikipedia’s response powerful wasn’t a central authority taking charge—it was ordinary people, working together, who refused to let truth be erased.
Another Front: The Croatian Wikipedia Takeover
The battle wasn’t just in German Wikipedia. In the 2010s, Croatian Wikipedia was hijacked from within. Nationalist administrators took control, rewriting history to downplay Croatia’s fascist past. Articles about the Ustaša, the country’s World War II fascist movement, were whitewashed. The concentration camp Jasenovac, where thousands of Serbs, Jews, and Roma were murdered, was falsely described as a “labor camp”.
Unlike in Germany, where an active community stopped the manipulation, Croatian Wikipedia was dominated by extremists for years. Editors who tried to correct falsehoods were banned. Only after public outcry from historians, journalists, and even the Wikimedia Foundation did the issue gain wider attention—but fixing the damage took years.
Why This Battle Still Matters
Wikipedia’s fight against manipulation is far from over. Right-wing groups continue to try to spread their version of history, and smaller Wikipedia editions remain especially vulnerable. But there’s hope:
– The Power of Transparency: Because Wikipedia is open, people can detect and correct manipulation.– Community Matters: Automated tools help, but human editors are the real defenders of truth.– We Need More Editors: Fewer people are actively contributing to Wikipedia, making it more vulnerable to future attacks. If young people stop editing, who will protect the truth?
Wikipedia’s volunteers showed that misinformation isn’t unbeatable. They proved that ordinary people can stand up to organized manipulation. But their success depends on one thing: a strong, engaged community.
This work is licensed under the Creative Common License. It can be republished for free, either translated or in the original language. In both cases, please cite Kontrast / Sarah Hammerschmid as the original source/author and set a link to this article on TheBetter.news. https://thebetter.news/wikipedia-fight-right-wing-manipulation/
The rights to the content remain with the original publisher. Läs mer…

The British city of Bradford proves that environmental protection benefits both public health and the economy. Since introducing its Clean Air Zone (CAZ) in 2022, the city has significantly improved air quality. The results speak for themselves: a 25% drop in doctor visits and annual healthcare savings exceeding €420,000.
Bradford Redefines Traffic Rules in Its Clean Air Zone – The Result: Cleaner Air and More Funding for Climate Action
When the English city of Bradford in Yorkshire introduced one of the country’s largest low-emission zones in 2022, reactions were mixed. Critics feared economic drawbacks, while supporters hoped for cleaner air and fewer health issues.
Two years later, a new study confirms the positive impact. The 22.4-square-kilometer Clean Air Zone (CAZ) is saving the UK’s healthcare system approximately £30,700 per month—more than €35,000 per month or €420,000 per year. According to the Bradford City Council, air pollution levels in the city are now the lowest ever recorded. Nitrogen dioxide levels have dropped, and doctor visits for respiratory and cardiovascular diseases have declined by 25 percent, amounting to 732 fewer medical appointments per month. This, in turn, helps to relieve pressure on the city’s overburdened emergency rooms and clinics.
What is particularly noteworthy is that the improvements extend beyond the Clean Air Zone itself. Many residents have upgraded to cleaner vehicles, leading to better air quality across the city. One striking example is Bradford’s taxi fleet, which is now the cleanest in the entire United Kingdom.
Who Has to Pay to Drive in the Clean Air Zone?
The CAZ regulates the use of older, high-emission buses, trucks, and taxis. These vehicles must either pay a daily fee or avoid the zone altogether:
•£50 (€58) per day for buses and trucks
•£9 (€10.50) per day for vans and minibuses
•£7 (€8) per day for taxis
Private cars and motorcycles are exempt from the charges.
Taxis, trucks, and commercial vehicles must pay fees to drive within Bradford’s Clean Air Zone. (Photo: Samuel Regan-Asante/Unsplash)
Investing in Cleaner Transportation
The revenue generated from these fees is reinvested directly into air quality improvement projects. The funds are used to modernize public transport, including upgrading to cleaner buses and introducing new electric vehicles on high-traffic routes. Taxi companies receive financial support to transition to low-emission vehicles, while businesses are offered grants to replace outdated, polluting vehicles.
Why Is Bradford’s Clean Air Zone More Effective Than London’s?
There are now more than 300 low-emission zones across the UK and Europe, but not all have been as successful as Bradford’s. In London, the Ultra-Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) was expanded to cover the entire city in August 2023, sparking widespread protests. The key difference is that London’s ULEZ also targets private cars that do not meet the latest emission standards, placing financial strain on many households.
Bradford took a different approach. The city actively supported businesses in transitioning to cleaner vehicles before the zone was implemented. The CAZ was also designed with social fairness in mind. Low-income communities are often the most affected by air pollution, despite contributing the least to it.
A study confirms this impact. “20% of the city population live inside the zone. These families tend to be the poorest, and most likely to suffer ill health. They are also less likely to cause pollution in the first place”, explains study leader Rosie McEachan.
This work is licensed under the Creative Common License. It can be republished for free, either translated or in the original language. In both cases, please cite The Better News / Sophie Wenkel as the original source/author and set a link to this article on TheBetter.news. https://thebetter.news/bradfords-clean-air-zone/
The rights to the content remain with the original publisher. Läs mer…

The Aral Sea was once one of the largest lakes in the world. But within just a few decades, human actions nearly dried it up. The surrounding regions in Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan have faced drought, soil salinization, and severe sandstorms. However, in recent years, international cooperation has given the Aral Sea a second chance. Large-scale water redirection, resilient vegetation, and a dam are driving the Aral Sea recovery.
Until the mid-20th century, the Aral Sea was the fourth-largest lake on Earth, covering 68,000 square kilometers—roughly the size of Ireland. But in the 1960s, disaster struck. The Soviet Union redirected the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers to irrigate vast cotton and rice fields. Without these rivers feeding it, the Aral Sea began to shrink rapidly. By the 1970s, it had already lost a significant amount of water. Today, only 10% of its original surface remains, while the Aralkum Desert has taken its place, growing to 62,000 square kilometers. This expanding desert brings extreme heat, salty soil, and dangerous sandstorms.
A Chain Reaction of Devastation
As the lake dried up, its remaining water became saltier, killing off most fish and plant life. Without the sea acting as a temperature regulator, summers now reach over 42°C, while winters are bitterly cold. A layer of salt formed on the exposed lakebed, preventing new plant growth. Strong winds lift this salt and sand into the air, spreading toxic dust laced with pesticides from old agricultural runoff. These storms have harmed human health and ecosystems across vast distances, even burying entire villages in sand.
[embedded content]
A Global Mission for Aral Sea Recovery
The water supply of the region depends on two major rivers: the Amu Darya, which flows through Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, and Afghanistan, and the Syr Darya, which runs through Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. With many Central Asian nations struggling with water shortages, international cooperation has become essential.
Since 2017, organizations such as the International Fund for Saving the Aral Sea and the Interstate Commission for Water Coordination in Central Asia have worked to manage water resources. In January 2025, a summit in Dushanbe, Tajikistan, resulted in a major agreement: Kazakhstan will receive 11 billion cubic meters of water through pipelines, with 1.6 billion cubic meters flowing directly into the Aral Sea by spring 2025.
Kazakhstan had already redirected 2.6 billion cubic meters of water to the Aral Sea in 2024. For comparison, in 2022, the amount was just 816 million cubic meters.
Saxaul Shrubs: Nature’s Answer to Desertification
To combat desertification, efforts have focused on reforesting parts of the former lakebed. Since 2021, the “Oasis” project, supported by U.S. development funds, has been planting saxaul shrubs on 500 hectares of land. These tough plants have deep roots that can hold up to 4,000 kilograms of sand, helping to stabilize the soil.
Unlike most vegetation, saxaul shrubs thrive in salty and arid conditions. Their tiny, scale-like leaves minimize water loss, making them ideal for the extreme environment. These shrubs reduce sand and salt storms, improve soil fertility, and create small patches of green in the desert.
[embedded content]
The Kok-Aral Dam: Engineering a Comeback
Another key project in saving the Aral Sea is the Kok-Aral Dam. Built in 2005 with financial backing from the World Bank, this 12-kilometer-long dam prevents water from flowing out of the northern part of the lake. Within just a few months, water levels rose by more than three meters, bringing significant ecological and economic benefits.
The fish population began to recover, and local businesses saw an economic boost. In Aralsk, a city that still lies 30 kilometers from its original waterfront, the dam has renewed hope. Investments in the region are increasing as the lake shows signs of revival.
The Return of Fish, Jobs, and Hope
One of the clearest signs of Aral Sea recovery is the return of fish. Between 1957 and 1987, annual fish catches plummeted from 48,000 tons to zero. With the construction of the Kok-Aral Dam, the lake’s salt levels stabilized, allowing fish to return. By 2018, fishing quotas had risen to 8,200 tons—a 600% increase compared to 2006. Läs mer…

Power outages – hardly imaginable in many parts of the world today. Yet in rural regions of East Africa, a lack of reliable energy was long an everyday reality. Today, however, communal solar power systems are transforming lives: they provide clean electricity that not only protects the climate but also improves health, education, and economic opportunities.
It’s nighttime at the Ndilidau Health Center in southeastern Kenya, near the border with Tanzania. Midwife Jacinta Malemba shines a flashlight into the darkness – just another of the countless nights when power outages disrupted the clinic’s operations. “We never lost anyone, but we often had to take great risks,” Jacinta recalls. The unreliable energy supply repeatedly brought the clinic’s work to a standstill: without electricity, equipment couldn’t be sterilized, vaccines and medicines couldn’t be refrigerated, and critical examinations had to be postponed.
Births in the Dark Are Now History
Today, the situation has changed dramatically. The small health center, serving twelve nearby villages with around 8,000 residents, now has its own solar power system, ensuring a reliable electricity supply. The impact on the community has been profound: pumps provide clean water for drinking and cooking, medical facilities can reliably operate their equipment, and local businesses benefit from stable energy access. These projects go far beyond basic power supply – they enhance education, healthcare, and economic growth.
Community Solar Power: A Collective Solution to Energy Poverty
The Ndilidau Health Center is one example in Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda where communal solar systems transform lives. These systems are often centrally installed for villages or household groups. Alternatively, they may operate as independent mini-grids, offering shared electricity access. Sharing power from one installation reduces costs and resource use while ensuring more sustainable energy solutions for communities.
In the Napenda Solar Community, located south of Nairobi, residents not only gain access to clean energy. They also also receive training on how solar systems work, how to build them, and how to maintain them. This knowledge empowers communities to operate and manage these systems independently for the long term. In rural regions without access to centralized power grids, such projects provide a reliable and sustainable energy supply.
[embedded content]
Solar vs. Kerosene and Diesel: Cleaner, Safer, More Affordable
Solar systems offer a sustainable alternative to kerosene and diesel generators, which were long the primary sources of electricity for many households. These traditional fuels not only harm health because of soot and smoke, but they also significantly damage the environment. Furthermore, they are inefficient, hazardous, and increasingly expensive over time. Communal solar systems, by contrast, are clean, safe, and cost-effective.
These systems often operate under a pay-as-you-go model: households pay a small deposit for installation, with subsequent usage costs settled in flexible, mobile installments. Well-known payment platforms like M-PESA, widely used in Kenya, facilitate this process. M-PESA enables users to make payments and transfers via mobile phones, even in areas without bank access.
A standout example is M-KOPA Solar, a Kenyan company offering solar solutions under this model. Customers first pay an initial fee of 35 USD. They then make daily payments of 0.45 USD, often lower than kerosene costs. After about a year, households fully own the solar system. This approach makes clean energy both accessible and practical. It also reduces costs and significantly improves living conditions, creating long-term benefits for families.
Bridging Africa’s Energy Gap with Solar Power
Globally, 1.3 billion people lack access to electricity, while another billion face unreliable supply. In Sub-Saharan Africa, about half the population lives without power. Off-grid solar systems could play a crucial role in bridging this gap. According to a study by the European Investment Bank and the International Solar Alliance, these systems could provide electricity to 120 million households across Africa.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts solar energy will dominate off-grid systems in Sub-Saharan Africa by 2040. Kenya aims to cut carbon emissions by 30% by 2030. The country promotes renewable energy through the National Climate Change Action Plan. Solar power combines climate action with innovation. It paves the way for a sustainable and fair energy future. Läs mer…
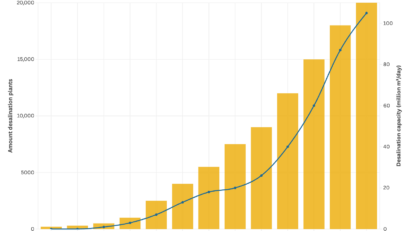
Amidst global water scarcity and the challenges posed by climate change, Morocco is turning to innovative solutions to secure water supplies for its population. A prominent example is the coastal city of Agadir, which is breaking new ground with one of the world’s most advanced seawater desalination plants. While the high energy demands of desalination are being met sustainably through renewable energy, a key question remains: Can seawater desalination be the answer to the global water crisis?
What is Seawater Desalination and Why is It Necessary?
Every child has wondered at some point why sailors can suffer from thirst while surrounded by water. The answer lies in the fact that not all water is drinkable: freshwater is essential for human survival, while drinking seawater, with its high salt content, dehydrates and harms the body. In a world where only about 3% of global water resources are freshwater—and much of that is locked in glaciers, groundwater, or hard-to-reach sources—ensuring an adequate freshwater supply is becoming increasingly challenging.
Seawater desalination offers a technical solution to convert saline water—primarily from the oceans—into potable freshwater. This process is particularly vital in regions with water scarcity or arid climates. According to a report by the International Desalination Association (IDA), the global capacity for seawater desalination has rapidly increased over the past few decades, with countries like Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Australia leading the way.
The amount of desalination plants and their capacities are constantly on the rise. Source: University of Leeds
As the global population continues to grow and climate change further stresses natural freshwater resources, desalination is becoming increasingly important. It serves not only as an emergency measure in water-scarce regions, but also as a strategy to secure future water supplies. However, the process is energy-intensive and poses environmental challenges, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable water management solutions.
Agadir: From Fishing Village to Pioneer in Seawater Desalination
Agadir, once a tranquil fishing village on Morocco’s Atlantic coast, has transformed into a major economic hub in recent decades. However, like many parts of Morocco, the city faces significant water challenges. Periods of drought, increasing water demand driven by agriculture and tourism, and the effects of climate change have pushed traditional water resources to their limits.
The Seawater Desalination Plant in Agadir: A Technological Marvel
Photo: James Grellier, Reverse osmosis desalination plant, CC BY-SA 3.0
To address these challenges, Agadir has built a state-of-the-art seawater desalination plant. This facility uses reverse osmosis, a process in which seawater is forced under high pressure through specialized membranes that remove salt, producing potable water. With a daily production capacity of 275,000 cubic meters of water—split into 150,000 cubic meters for drinking water and 125,000 cubic meters for irrigation—it ranks among the largest of its kind globally. The plant’s capacity can be expanded to 400,000 cubic meters per day if needed.
The project was realized through a public-private partnership between Morocco’s National Office for Electricity and Drinking Water (ONEE) and the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries, Rural Development, Water, and Forests. In 2019, it was recognized by the IDA as the “Best Public-Private Partnership.”
Utilizing Renewable Energy: A Focus on Sustainability
A distinctive feature of the Agadir plant is the sole operation with renewable energy. Thanks to the intense sunlight and strong winds along Morocco’s coast, the facility is entirely powered by solar and wind energy. This not only reduces operational costs, but also significantly minimizes the plant’s environmental footprint, making it a model for sustainable water production.
Positive Impact of Seawater Desalination for the Region
The desalination plant in Agadir has already brought significant and sustainable change to the region. It has secured a reliable drinking water supply for over half a million people, providing a consistent source of clean water independent of climatic or seasonal fluctuations. Beyond residential needs, the agricultural lands in the Chtouka Plain surrounding Agadir also benefit. The daily supply of treated water for irrigation has boosted productivity and strengthened the economic foundation of local agriculture.
The construction and operation of the plant have also created numerous jobs, contributing to the regional economy. Moreover, the plant has significantly improved the quality of life for residents. With stable access to drinking water and a fortified agricultural base, the plant not only ensures supply but also enhances resilience against the challenges posed by climate change.
Not All That Glitters is Gold: Challenges of Seawater Desalination
Despite its advantages, seawater desalination faces some challenges. One major criticism is the high energy demand of desalination plants. The process consumes large amounts of electricity, making it expensive and potentially harmful to the environment when fossil fuels are used. Although modern plants like the one in Agadir increasingly rely on renewable energy, such projects remain the exception. The majority of desalination plants worldwide still depend on conventional energy sources. While reverse osmosis is more energy-efficient than older technologies, it still requires considerable power to operate.
Another issue is brine, a highly concentrated byproduct of desalination. Many plants discharge this brine back into the ocean, where it can harm local ecosystems. The increased salinity and chemicals used during water pretreatment can damage marine habitats and threaten biodiversity. Solutions for the safe disposal or reuse of brine are under development. However, they are currently only available on a limited scale.
Is Desalination a Model for Other Regions?
The successful implementation of Agadir’s desalination plant serves as a model for other water-scarce regions worldwide. The integration of desalination technology with renewable energy could be particularly applicable in coastal areas with similar climatic conditions. Morocco is already planning to expand its network of desalination plants to combat water scarcity nationwide.
This work is licensed under the Creative Common License. It can be republished for free, either translated or in the original language. In both cases, please cite Kontrast / Justus Hartmann as the original source/author and set a link to this article on TheBetter.news. https://thebetter.news/seawater-desalination-in-agadir/
The rights to the content remain with the original publisher. Läs mer…