Cleaner Air, Healthier Lives: Bradford’s Clean Air Zone Success
The British city of Bradford proves that environmental protection benefits both public health and the economy. Since introducing its Clean Air Zone (CAZ) in 2022, the city has significantly improved air quality. The results speak for themselves: a 25% drop in doctor visits and annual healthcare savings exceeding €420,000.
Bradford Redefines Traffic Rules in Its Clean Air Zone – The Result: Cleaner Air and More Funding for Climate Action
When the English city of Bradford in Yorkshire introduced one of the country’s largest low-emission zones in 2022, reactions were mixed. Critics feared economic drawbacks, while supporters hoped for cleaner air and fewer health issues.
Two years later, a new study confirms the positive impact. The 22.4-square-kilometer Clean Air Zone (CAZ) is saving the UK’s healthcare system approximately £30,700 per month—more than €35,000 per month or €420,000 per year. According to the Bradford City Council, air pollution levels in the city are now the lowest ever recorded. Nitrogen dioxide levels have dropped, and doctor visits for respiratory and cardiovascular diseases have declined by 25 percent, amounting to 732 fewer medical appointments per month. This, in turn, helps to relieve pressure on the city’s overburdened emergency rooms and clinics.
What is particularly noteworthy is that the improvements extend beyond the Clean Air Zone itself. Many residents have upgraded to cleaner vehicles, leading to better air quality across the city. One striking example is Bradford’s taxi fleet, which is now the cleanest in the entire United Kingdom.
Who Has to Pay to Drive in the Clean Air Zone?
The CAZ regulates the use of older, high-emission buses, trucks, and taxis. These vehicles must either pay a daily fee or avoid the zone altogether:
•£50 (€58) per day for buses and trucks
•£9 (€10.50) per day for vans and minibuses
•£7 (€8) per day for taxis
Private cars and motorcycles are exempt from the charges.
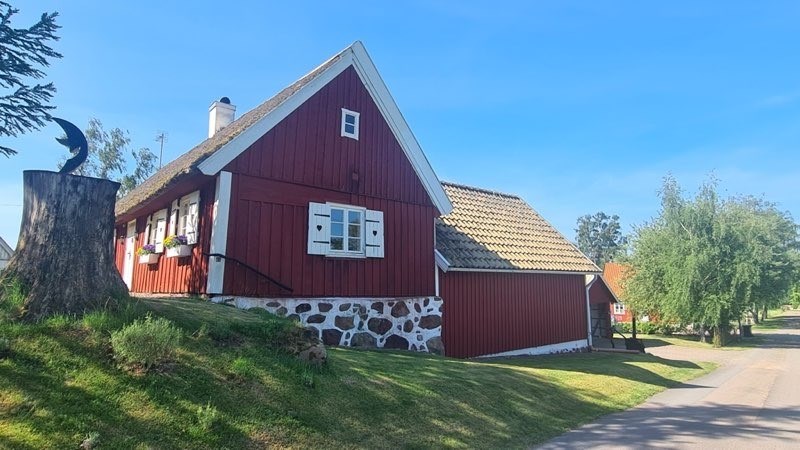
Taxis, trucks, and commercial vehicles must pay fees to drive within Bradford’s Clean Air Zone. (Photo: Samuel Regan-Asante/Unsplash)
Investing in Cleaner Transportation
The revenue generated from these fees is reinvested directly into air quality improvement projects. The funds are used to modernize public transport, including upgrading to cleaner buses and introducing new electric vehicles on high-traffic routes. Taxi companies receive financial support to transition to low-emission vehicles, while businesses are offered grants to replace outdated, polluting vehicles.
Why Is Bradford’s Clean Air Zone More Effective Than London’s?
There are now more than 300 low-emission zones across the UK and Europe, but not all have been as successful as Bradford’s. In London, the Ultra-Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) was expanded to cover the entire city in August 2023, sparking widespread protests. The key difference is that London’s ULEZ also targets private cars that do not meet the latest emission standards, placing financial strain on many households.
Bradford took a different approach. The city actively supported businesses in transitioning to cleaner vehicles before the zone was implemented. The CAZ was also designed with social fairness in mind. Low-income communities are often the most affected by air pollution, despite contributing the least to it.
A study confirms this impact. “20% of the city population live inside the zone. These families tend to be the poorest, and most likely to suffer ill health. They are also less likely to cause pollution in the first place”, explains study leader Rosie McEachan.
This work is licensed under the Creative Common License. It can be republished for free, either translated or in the original language. In both cases, please cite The Better News / Sophie Wenkel as the original source/author and set a link to this article on TheBetter.news. https://thebetter.news/bradfords-clean-air-zone/
The rights to the content remain with the original publisher. Läs mer…